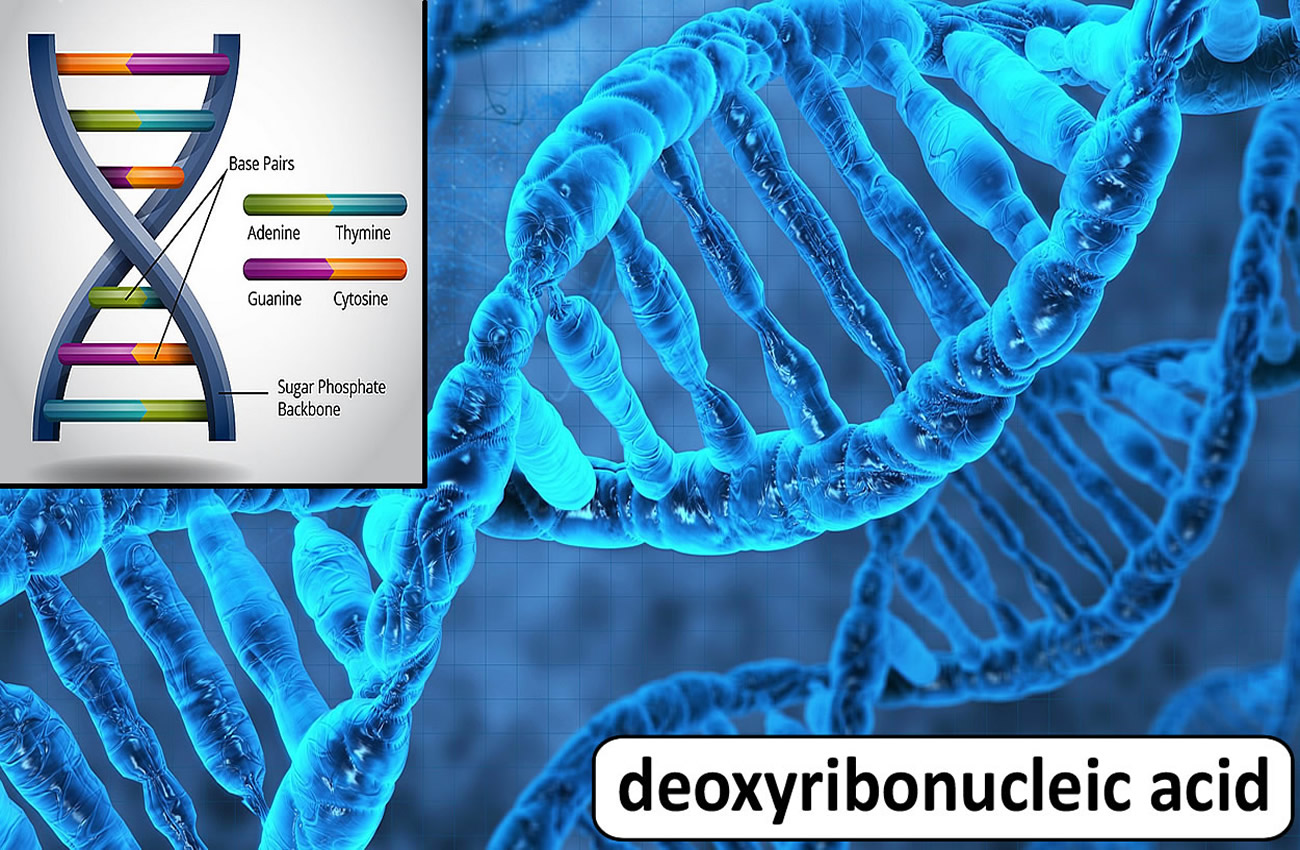
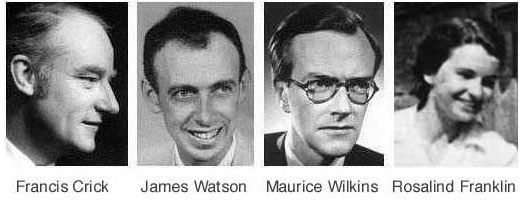????????? is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. Nearly every cell in a person's body has the same ?????????. The information in ????????? is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). ????????? is vital for all living beings – even plants. It is important for inheritance, coding for proteins and the genetic instruction guide for life and its processes. ????????? holds the instructions for an organism's or each cell's development and reproduction and ultimately death. ????????? profiling is a forensic technique in criminal investigations, comparing criminal suspects' profiles to ????????? evidence so as to assess the likelihood of their involvement in the crime. It is also used in parentage testing, to establish immigration eligibility, and in genealogical and medical research. SEE RIGHT: Much research on this subject had been done before; some in the 19th century, but it was this team that finally cracked it on February 28th, 1953. Watson & Crick realized the double-helix structure of ????????? using an X-Ray from Rosalind Franklin. The first two won the Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 1962, but Rosalind was left out. She died in April 1958 only 38 years old. |